Introduction
Globally, developers wrote an incredible 256 billion lines of code in 2024; by 2025, that figure is expected to rise to 600 billion. This rapid expansion isn’t just about volume; it also represents a fundamental change in how companies function, with web applications serving as the foundation for digital transformation.
You’re probably using a web application whether ordering takeout, checking your bank account, or working with coworkers. However, what is web application development, and why is it so crucial for today’s companies?
This comprehensive guide will demystify web application development by thoroughly explaining everything from fundamental ideas to sophisticated implementation techniques. It will cover the entire development process, necessary tools, and new trends that will change the industry in 2025.
What is Web Application Development?

Web application development involves creating application programs that run on distant servers and are sent to the user’s device via the Internet. Unlike traditional desktop apps, which need to be installed, web apps are accessible over a network and don’t need to be downloaded.
Web application development is creating, developing, and maintaining unique web applications in web browsers. These apps can be accessed on various devices, such as PCs, smartphones, and tablets, via private networks or the Internet.
Key Characteristics of Web Applications
Browser-Based Access: Without locally installing software, users use web browsers to interact with web applications.
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Web applications run reliably on various devices and operating systems.
Real-Time Updates: Since changes and updates are implemented server-side, all users will always have instant access to the most recent version.
Centralised Data Management: The processing and storage of information on distant servers make data synchronisation and collaboration possible.
Types of Web Applications
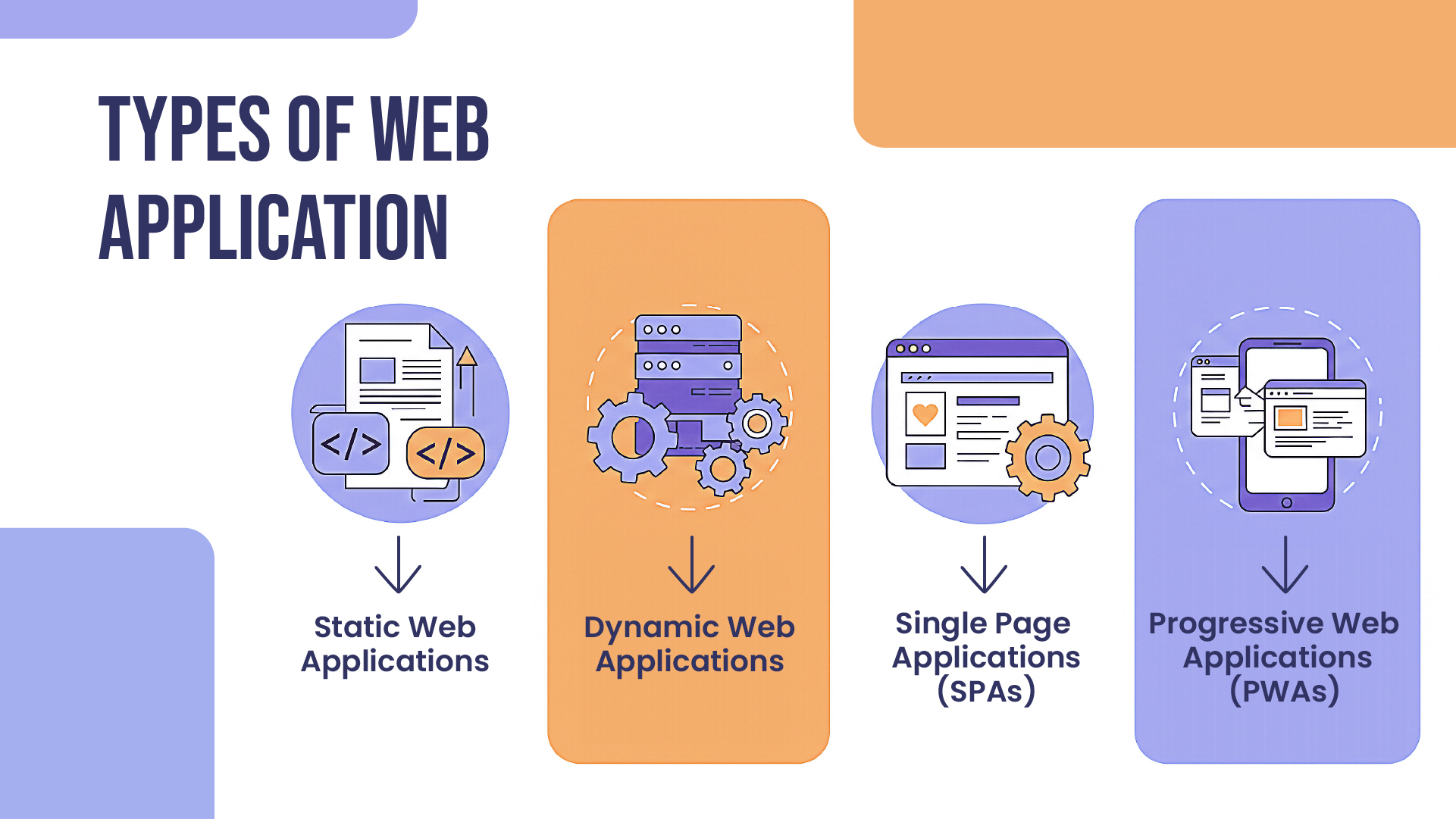
Static Web Applications
Static web applications show pre-made content that developers must manually update. These consist of:
- Business websites
- Websites for portfolios
- Simple landing pages
Dynamic Web Applications
Real-time content generation by dynamic web applications is dependent on user input, database queries, or outside data sources:
- E-commerce platforms
- Social media platforms
- Systems for managing content
Single Page Applications (SPAs)
SPAs offer a smooth user experience by dynamically loading content without requiring a page refresh:
- Gmail
Progressive Web Applications (PWAs)
PWAs offer offline functionality and native-like experiences by combining the best aspects of web and mobile applications:
- Starbucks PWA
- Uber
The Web Application Development Process
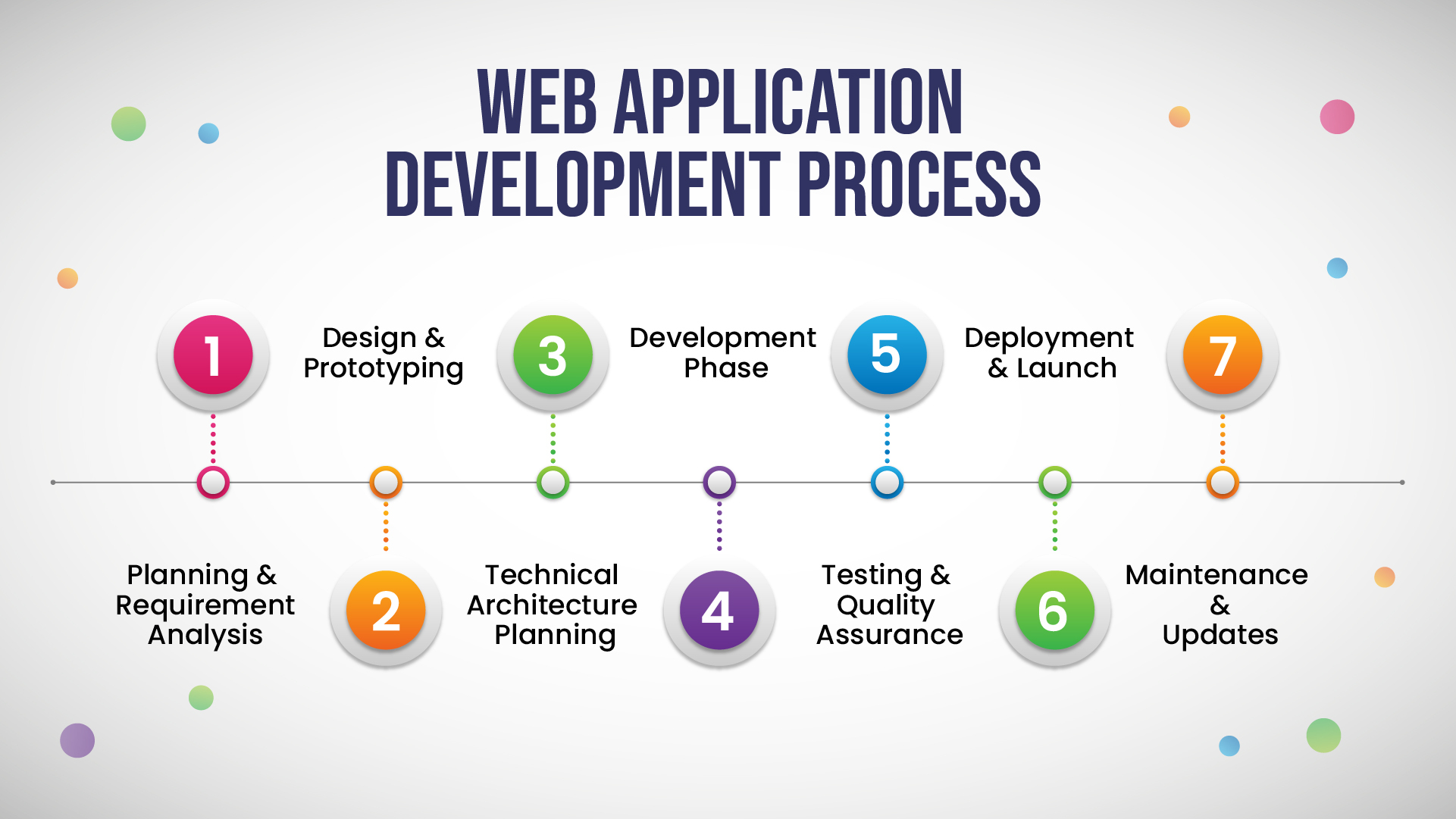
1. Planning and Requirements Analysis
Set project goals: Clearly state your objectives, target audience, and metrics for success.
Assemble the required supplies: Using stakeholder interviews and market research, document functional and non-functional requirements.
Create a project timeline: Establish logical milestones and delivery schedules.
2. Design and Prototyping
User Experience (UX) Design: Make wireframes, journey maps, and user personas.
User Interface (UI) Design: Create colour palettes, branding components, and visual mockups.
Prototyping: Create interactive prototypes to get user input and validate design ideas.
3. Technical Architecture Planning
Technology Stack Selection: Select the right databases, frameworks, and programming languages.
System Architecture Design: Arrange the data flow, server infrastructure, and API structures.
Security Planning: Put authorisation, authentication, and data security measures into practice..
4. Development Phase
Frontend Development
- Languages: HTML5, CSS3, JavaScript
- Frameworks: React, Angular, Vue.js
- Responsive Design: Ensure compatibility across devices and screen sizes
Backend Development
- Server-Side Languages: Python, Node.js, PHP, Java, C#
- Database Management: PostgreSQL, MongoDB, MySQL
- API Development: RESTful APIs, GraphQL
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
Unit Testing: Test specific parts and features.
Integration Testing: Check the data flow and component interactions.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Verify that the application satisfies the business needs.
Performance Testing: Evaluate scalability, speed, and load handling.
6. Deployment and Launch
Environment Setup: Set up deployment pipelines and production servers.
Domain and Hosting: Dependable hosting services and safe domain names.
SSL Certificate Installation: Make sure that data is transmitted securely.
7. Maintenance and Updates
Regular Monitoring: Monitor user comments, security, and performance.
Feature Updates: Implement new features in accordance with user requirements.
Security Patches: Keep your security measures current.
Essential Technologies and Tools
Frontend Technologies
| Technology | Purpose | Popular Frameworks |
| HTML5 | Structure and content | – |
| CSS3 | Styling and layout | Bootstrap, Tailwind CSS |
| JavaScript | Interactivity and logic | React, Angular, Vue.js |
| TypeScript | Type-safe JavaScript | Angular, React with TS |
Backend Technologies
| Language | Use Cases | Popular Frameworks |
| JavaScript (Node.js) | Full-stack development | Express.js, Next.js |
| Python | Data-heavy applications | Django, Flask |
| PHP | Web-focused development | Laravel, Symfony |
| Java | Enterprise applications | Spring Boot |
| C# | Microsoft ecosystem | ASP.NET Core |
Database Options
Relational Databases:
- PostgreSQL: Robust, open-source
- MySQL: Popular, user-friendly
- SQL Server: Enterprise-grade Microsoft solution
NoSQL Databases:
- MongoDB: Document-oriented, flexible
- Redis: In-memory, high-performance
- Firebase: Real-time, cloud-based
Development Tools
Code Editors: Visual Studio Code, WebStorm, Sublime Text
Version Control: Git, GitHub, GitLab
Project Management: Jira, Trello, Asana
API Testing: Postman, Insomnia
Performance Monitoring: Google Analytics, New Relic
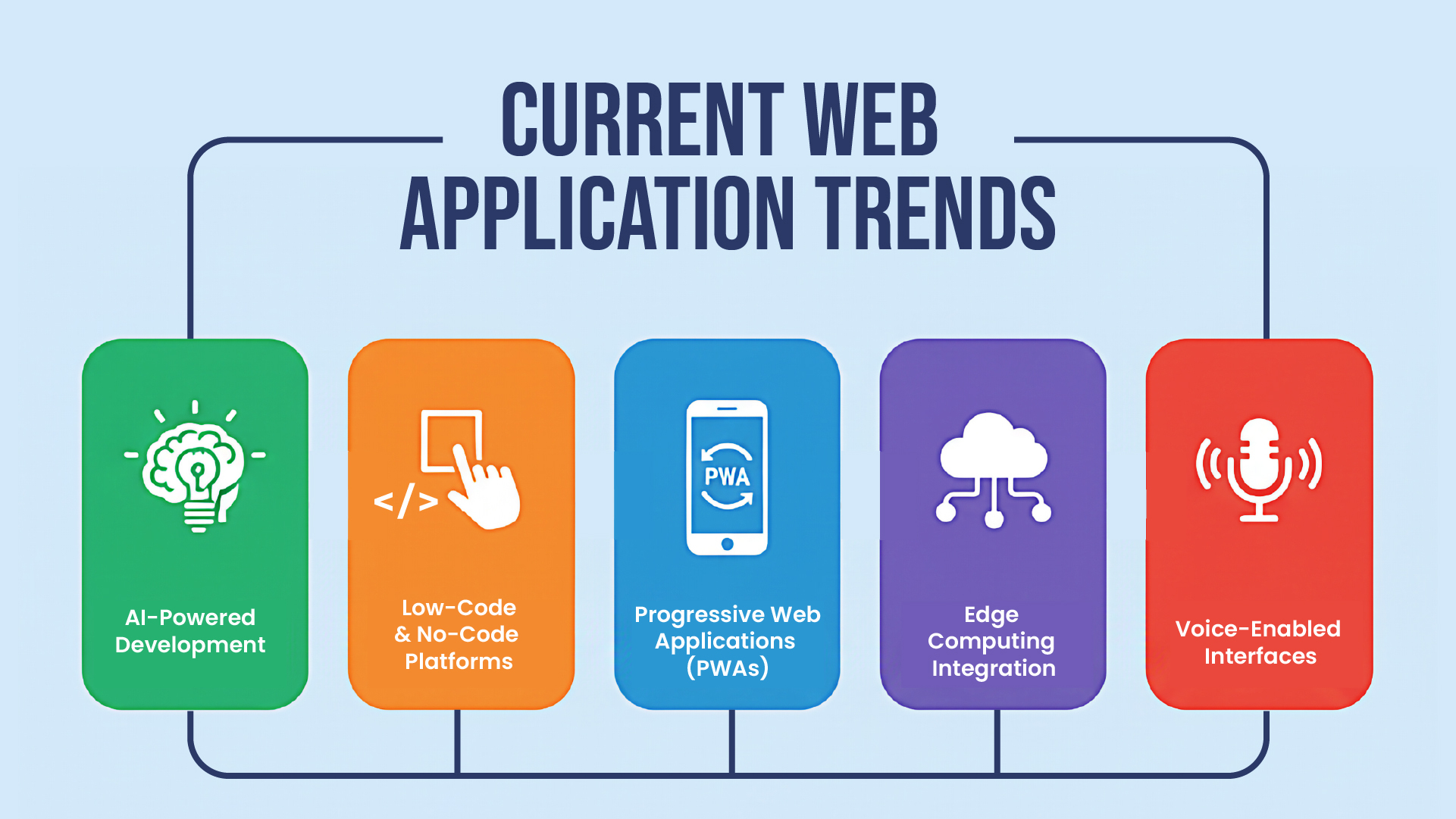
Current Trends in Web Application Development (2025)
1. AI-Powered Development
AI is expected to help generate 90% of all code by 2026. Development is being revolutionised by AI tools through:
- Automated code generation
- Debugging with intelligence
- Integration of predictive analytics
- Enhanced customisation for users
2. Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
More than 70% of new web applications will use low-code or no-code tools by 2025, predicts Gartner. This pattern makes it possible for:
- Faster development cycles
- Reduced development costs
- Greater accessibility for non-technical users
- Rapid prototyping and iteration
3. Progressive Web Applications (PWAs)
PWAs are still becoming more popular because they can:
- Function offline
- Send push notifications
- Provide native app-like experiences
- Improve user engagement and retention
4. Edge Computing Integration
75% of enterprise data processing will move from centralised data centres to the edge by 2025. This change provides:
- Reduced latency
- Improved performance
- Better data privacy
- Enhanced user experiences
5. Voice-Enabled Interfaces
In the upcoming years, voice searches will account for over half of all internet searches, necessitating:
- Voice user interface (VUI) integration
- Natural language processing capabilities
- Accessibility improvements
- Hands-free interaction options
Benefits of Professional Web Application Development
For Businesses
Increased Reach: Access global markets without geographical limitations.
Cost Efficiency: Web apps are less costly to develop than native apps, as they employ a single user interface and back-end systems for users across all platforms.
Scalability: Easily accommodate growing user bases and feature requirements.
Data Insights: Gather valuable analytics on user behavior and application performance.
For Users
Accessibility: Access applications from any device with an internet connection.
Automatic Updates: Always use the latest version without manual installations.
Cross-Platform Consistency: Enjoy consistent experiences across different devices.
Real-Time Collaboration: Work with others simultaneously on shared projects and data.
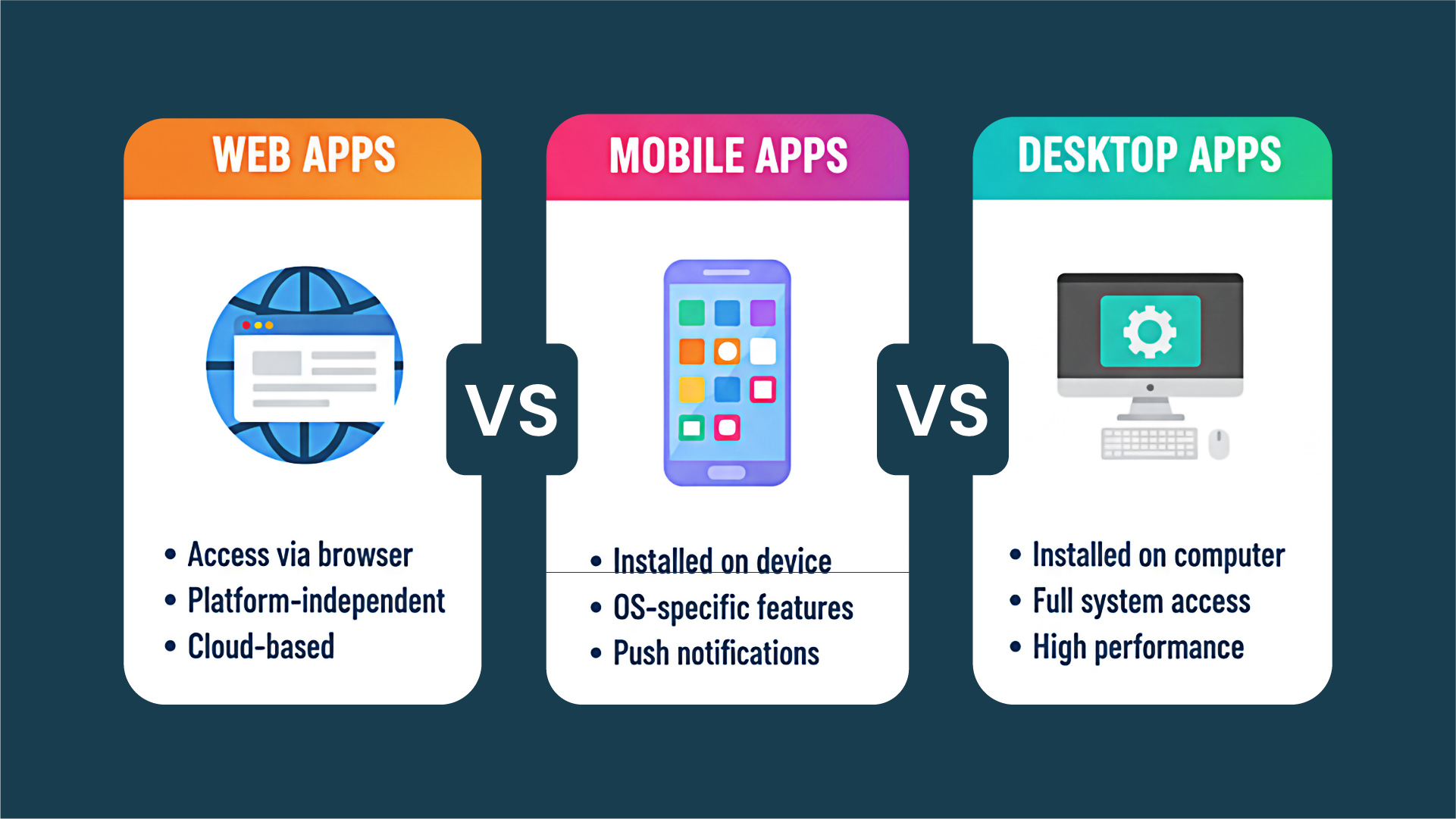
Web Application Development vs. Other Development Types
| Aspect | Web Applications | Mobile Apps | Desktop Applications |
| Platform | Cross-platform via browsers | Platform-specific (iOS/Android) | Operating system specific |
| Installation | No installation required | App store installation | Software installation needed |
| Updates | Automatic server-side updates | Manual app store updates | Manual software updates |
| Development Cost | Moderate | Higher (separate iOS/Android) | Moderate to high |
| Maintenance | Centralized maintenance | Multiple platform maintenance | Individual system maintenance |
| Performance | Good for most use cases | Optimized for mobile hardware | Optimized for desktop hardware |
Security Considerations in Web Application Development
Common Security Threats
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): Malicious scripts injected into trusted websites.
SQL Injection: Unauthorized database access through vulnerable input fields.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF): Unauthorized actions performed on behalf of authenticated users.
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive user information.
Security Best Practices
- Input Validation: Sanitize and validate all user inputs
- Authentication and Authorization: Implement secure user verification systems
- HTTPS Implementation: Encrypt data transmission with SSL/TLS certificates
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct penetual testing and vulnerability assessments
- Data Encryption: Protect sensitive data both in transit and at rest
Cost Factors in Web Application Development
Development Phase Costs
Planning and Design: 15-25% of total budget Frontend Development: 25-35% of total budget
Backend Development: 25-35% of total budget Testing and QA: 10-15% of total budget Deployment and Setup: 5-10% of total budget
Ongoing Costs
Infrastructure and hosting: $50–$500+ a month. Domain registration costs between $10 and $50 annually. SSL certificates cost between $50 and $200 annually. Updating and maintenance: 15% to 20% of the original development cost per year. Third-Party Integrations: Dependent on the services utilised.
Factors Affecting Development Costs
- Application Complexity: Simple vs. enterprise-level applications
- Feature Requirements: Basic functionality vs. advanced features
- Technology Stack: Open-source vs. premium tools and frameworks
- Development Team Location: Regional cost variations
- Timeline Requirements: Standard vs. accelerated development schedules
Get in touch with our development team to discuss your needs and obtain a personalised proposal for a comprehensive cost estimate for your particular project.
Conclusion
From basic static pages to complex platforms driven by artificial intelligence, web application development has advanced to power contemporary business operations. The need for qualified web application developers is only expected to grow as developers will write 600 billion lines of code by 2025.
Understanding web application development is essential for success in today’s digital environment, regardless of whether you’re a startup trying to build your online presence or an enterprise looking to update outdated systems. Selecting the appropriate technologies, adhering to best practices, and collaborating with skilled developers who can realise your vision are crucial.
Are you prepared to create your next web application? The knowledgeable development staff at Desol Int is available to assist you in navigating the challenges of contemporary web development. We offer complete solutions that are suited to your company’s requirements, from the original concept to continuing upkeep. Schedule a free consultation right now to find out how we can turn your ideas into practical web applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How long does it take to develop a web application?
The development timeline varies based on project complexity. Simple applications may take 2-4 months, while complex enterprise solutions can require 6-12 months or more. Factors affecting the timeline include feature requirements, integration needs, team size, and approval processes.
2. What’s the difference between a website and a web application?
Websites primarily display information and have limited interactivity, while web applications provide dynamic functionality allowing users to perform tasks, manipulate data, and interact with databases. Web applications are more complex and require more sophisticated development approaches.
3. How much does web application development cost?
Development costs range from $10,000 for simple applications to $100,000+ for complex enterprise solutions. Factors influencing cost include application complexity, feature requirements, technology stack, development team location, and timeline constraints.
4. Which programming language is best for web application development?
The best language depends on project requirements. JavaScript (with Node.js) offers full-stack development, Python excels for data-heavy applications, PHP remains popular for web-focused development, and Java suits enterprise applications. Consider factors like team expertise, project complexity, and scalability needs.
5. How do I maintain and update my web application after launch?
Regular maintenance includes security updates, performance monitoring, bug fixes, feature enhancements, and content updates. Establish monitoring systems, schedule regular backups, implement security patches promptly, and gather user feedback for continuous improvement.
Overwhelmed by Options?
Let Desol Build It For You!
Skip the research. Contact the experts at Desol Int — we’ll build the perfect form for your business needs.
★★★★★
Trusted by 2,800+ businesses worldwide.
