Introduction
Did you know that projects using Joint Application Development (JAD) methodology report improvements in requirements definition and IS efficiency in 10-30% of cases examined? Yet, many organizations still struggle with traditional development approaches that disconnect end-users from the development process.
Created by Arnie Lind, a Senior Systems Engineer at IBM Canada in 1974, JAD emerged as a solution to a persistent problem: applications that took years to develop and were often not fully accepted by users. Traditional methods required developers to spend months learning job functions before creating applications, leading to significant delays and user dissatisfaction.
If you’ve ever wondered why some software projects succeed while others fail spectacularly, the answer often lies in how well developers understand user needs. This comprehensive guide will explore Joint Application Development, its benefits, implementation process, and why it might be the methodology your next project needs.
What is Joint Application Development (JAD)?

Joint Application Development (JAD) is a methodology that involves the client or end user in designing and developing a software application through a succession of collaborative workshops called JAD sessions.
Unlike traditional development approaches, where developers work in isolation, JAD brings together all stakeholders, including end-users, business analysts, developers, and project managers, to collaborate directly in structured workshop environments.
Core Principles of JAD
The JAD methodology is built on four fundamental principles:
- Collaborative Design: All stakeholders participate in the design process
- Structured Workshops: Organized sessions with specific objectives and outcomes
- User-Centered Focus: End-users drive requirements and validate solutions
- Consensus Building: Decisions are made collectively through structured discussion
How JAD Differs from Traditional Development
| Aspect | Traditional Development | Joint Application Development |
| User Involvement | Limited to requirements gathering | Continuous throughout development |
| Communication | Formal documentation | Face-to-face workshops |
| Feedback Loop | End-of-cycle testing | Real-time validation |
| Time to Market | Longer development cycles | Accelerated delivery |
| User Satisfaction | Often requires post-launch changes | Higher acceptance rates |
The JAD Process: Step-by-Step Guide
Phase 1: Pre-Workshop Planning (1-2 Weeks)
Stakeholder Identification
- End Users: People who will actually use the system
- Subject Matter Experts: Business process owners
- Technical Team: Developers, architects, analysts
- Decision Makers: Managers with authority to approve changes
Workshop Preparation
- Define project scope and objectives
- Prepare background materials and documentation
- Schedule sessions with all stakeholders
- Arrange suitable workshop facilities
Phase 2: JAD Workshop Sessions (3-5 Days)
Day 1: Project Overview and Ground Rules
- Establish workshop objectives
- Review project background
- Set communication protocols
- Begin high-level requirements discussion
Days 2-3: Detailed Requirements Gathering
- Map current business processes
- Identify pain points and improvement areas
- Define functional and non-functional requirements
- Create user stories and use cases
Days 4-5: Design and Validation
- Develop system design concepts
- Create mockups and prototypes
- Validate solutions against requirements
- Plan implementation approach
Phase 3: Post-Workshop Documentation (1-2 Weeks)
- Compile workshop outcomes into formal specifications
- Create detailed project documentation
- Develop project timeline and milestones
- Distribute materials to all stakeholders
Key Benefits of Joint Application Development
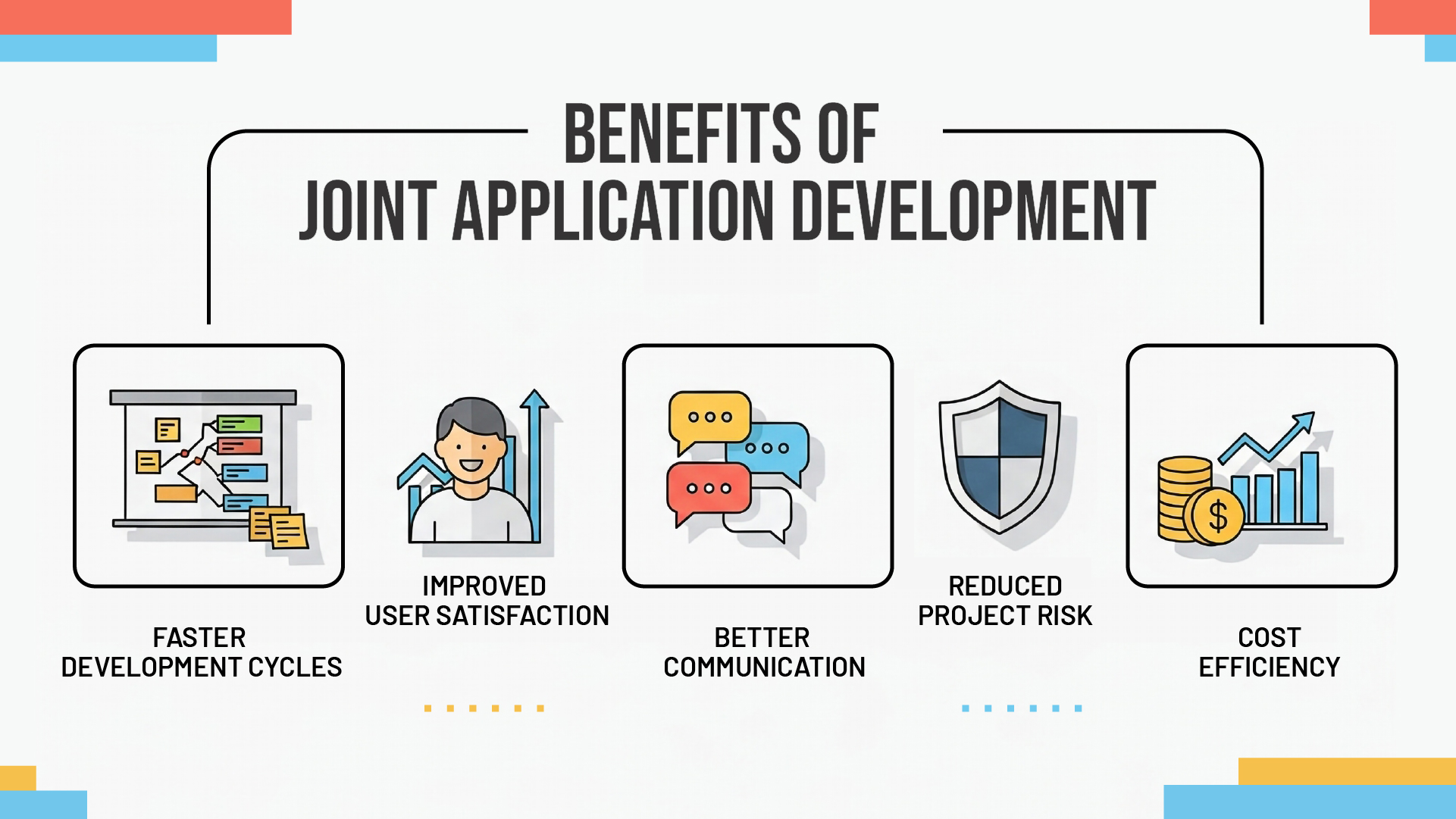
1. Faster Development Cycles
The JAD approach leads to faster development times than traditional practices because the client is involved throughout the development process. By addressing requirements and design issues upfront, teams avoid costly late-stage revisions.
2. Improved User Satisfaction
This collaborative approach ensures comprehensive requirement gathering, reduces misunderstandings, and creates stakeholder buy-in that improves implementation success rates.
3. Better Communication
JAD breaks down silos between technical teams and business users, fostering understanding and collaboration that extends beyond individual projects.
4. Reduced Project Risk
Early identification of issues and continuous stakeholder involvement significantly reduce the risk of project failure or major post-launch modifications.
5. Cost Efficiency
Benefits include savings on time and resources, and system requirements written through cooperation between future users and IT development teams.
JAD Methodology Components
1. JAD Sessions Structure
Session Roles
- Session Leader/Facilitator: Guides discussions and manages the process
- Scribe: Documents decisions and action items
- Participants: Contribute expertise and make decisions
- Observers: Learn but don’t actively participate
Session Techniques
- Brainstorming: Generate ideas without immediate evaluation
- Storyboarding: Visual representation of user interactions
- Prototyping: Create working models for validation
- Prioritization: Rank features and requirements by importance
2. Documentation Standards
Requirements Documentation
- Functional specifications
- User interface designs
- Business process flows
- Technical architecture diagrams
Decision Tracking
- Meeting minutes with decisions made
- Action item assignments
- Change request logs
- Risk and issue registers
JAD vs Other Development Methodologies
JAD vs Agile Development
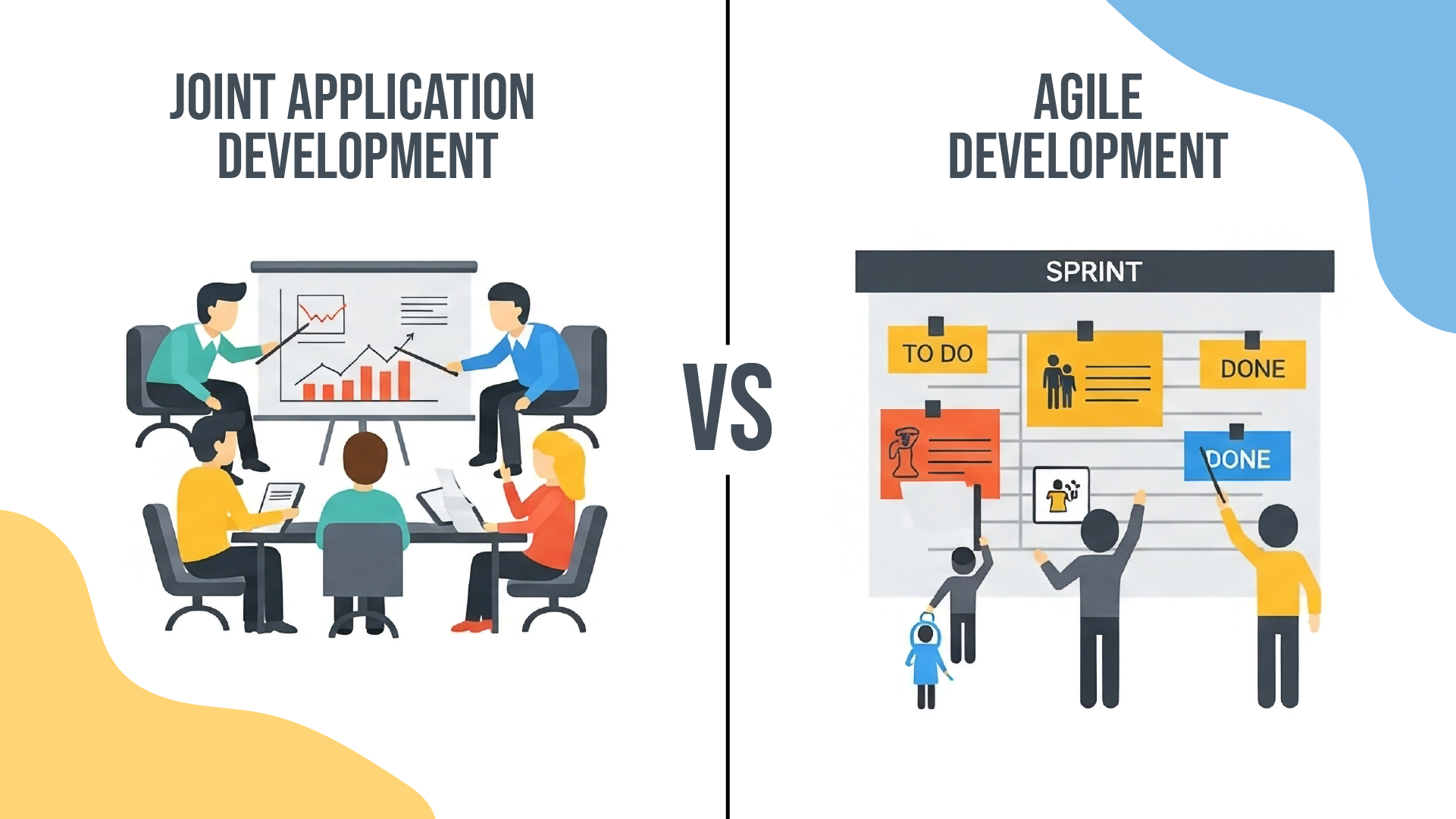
| Factor | JAD | Agile |
| Workshop Intensity | Intensive upfront sessions | Ongoing short meetings |
| Documentation | Comprehensive specifications | Minimal documentation |
| Change Management | Structured change process | Embraces continuous change |
| User Involvement | Concentrated involvement | Distributed throughout sprints |
JAD vs Waterfall
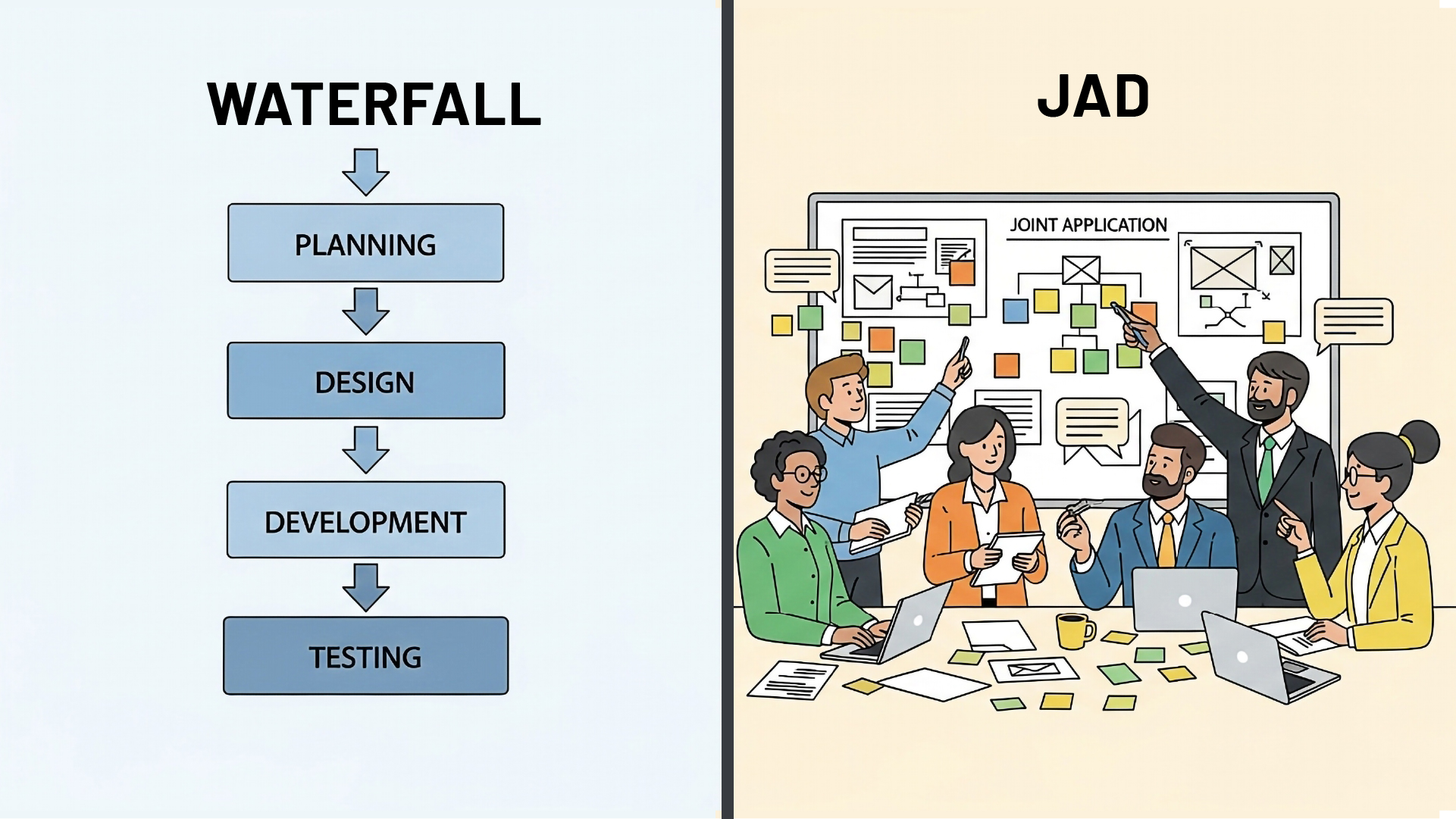
| Factor | JAD | Waterfall |
| User Input | Collaborative workshops | Limited to the requirements phase |
| Flexibility | Moderate adaptability | Rigid structure |
| Validation | Continuous throughout the workshops | End-of-phase reviews |
| Risk Management | Early identification | Later-stage discovery |
JAD vs Rapid Application Development (RAD)

The JAD methodology emphasizes structured collaboration through workshops with key stakeholders, ensuring comprehensive and consensus-driven project requirements. Conversely, RAD prioritizes speed and flexibility, utilizing rapid prototyping.
Best Practices for Successful JAD Implementation
1. Preparation is Critical
- Select the Right Participants: Include decision-makers with authority
- Prepare Thoroughly: Gather background information before sessions
- Set Clear Objectives: Define what success looks like for each session
2. Facilitate Effectively
- Maintain Focus: Keep discussions on track and productive
- Encourage Participation: Ensure all voices are heard
- Document Everything: Capture decisions and rationale in real-time
3. Follow Through
- Distribute Documentation Promptly: Share outcomes within 48 hours
- Track Action Items: Assign ownership and due dates
- Validate Understanding: Confirm interpretation with stakeholders
4. Manage Expectations
- Set Realistic Timelines: Don’t overpromise on deliverables
- Communicate Changes: Keep all stakeholders informed of modifications
- Plan for Iterations: Build flexibility into the process
Common Challenges and Solutions

Challenge 1: Scheduling Conflicts
Solution: Schedule sessions well in advance and emphasize the importance of attendance. Consider multiple shorter sessions if needed.
Challenge 2: Dominant Personalities
Solution: Use structured facilitation techniques to ensure balanced participation. Set ground rules for respectful discussion.
Challenge 3: Technical Complexity
Solution: Prepare technical concepts in advance and use visual aids to explain complex systems to non-technical participants.
Challenge 4: Scope Creep
Solution: Establish clear boundaries and use structured change management processes for new requirements.
When to Use JAD Methodology
Ideal JAD Projects
JAD works best for projects with these characteristics:
- Complex business requirements requiring multiple stakeholder input
- High user interaction systems where usability is critical
- Cross-functional impact affecting multiple departments
- Tight deadlines requiring accelerated development
- High-visibility projects where stakeholder buy-in is essential
When JAD May Not Be Suitable
- Simple applications with straightforward requirements
- Projects with unchanging, well-documented processes
- Situations where key stakeholders cannot commit time
- Highly technical projects with minimal user interaction
Measuring JAD Success
Key Performance Indicators
Project Metrics
- Time to Market: Reduction in development timeline
- Budget Adherence: Staying within financial constraints
- Scope Stability: Minimizing late-stage requirement changes
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: User acceptance and approval ratings
Quality Metrics
- Defect Rate: Post-launch issues and bug reports
- User Adoption: Speed of system acceptance and usage
- Training Requirements: Reduced need for extensive user training
- Maintenance Costs: Lower ongoing support requirements
Success Stories and Case Studies
Due to close interactions, progress is faster. JAD helps to accelerate design and enhance quality. Organizations implementing JAD have reported:
- 30-50% reduction in development time
- 25% decrease in post-launch defects
- 40% improvement in user satisfaction scores
- Significant reduction in training and support costs
JAD Tools and Technologies
Workshop Facilitation Tools
Physical Workshop Tools
- Whiteboards and flip charts for brainstorming
- Sticky notes for prioritization exercises
- Projectors for screen sharing and presentations
- Conference room setup for collaborative discussion
Digital Collaboration Platforms
- Miro/Mural: Visual collaboration for remote workshops
- Microsoft Teams/Zoom: Video conferencing with breakout rooms
- Confluence/SharePoint: Documentation and knowledge sharing
- Jira/Azure DevOps: Requirements tracking and project management
Documentation and Modeling Tools
- Visio/Lucidchart: Process flow and system diagrams
- Figma/Sketch: User interface mockups and prototypes
- Enterprise Architect: Technical architecture modeling
- Requirements management tools: For tracking and validation
Expert Implementation at Desol Int.
At Desol Int we’ve successfully implemented JAD methodology across numerous projects, helping organizations achieve faster delivery and higher user satisfaction. Our experienced team understands that successful JAD implementation requires more than just scheduling workshops, it demands skilled facilitation, structured processes, and careful stakeholder management.
Our custom application development approach integrates JAD principles with modern agile practices, creating hybrid methodologies that deliver the collaborative benefits of JAD while maintaining the flexibility needed for today’s dynamic business environment.
Whether you’re looking to improve an existing development process or implement JAD for the first time, our team can guide you through every step of the journey.
Future of Joint Application Development
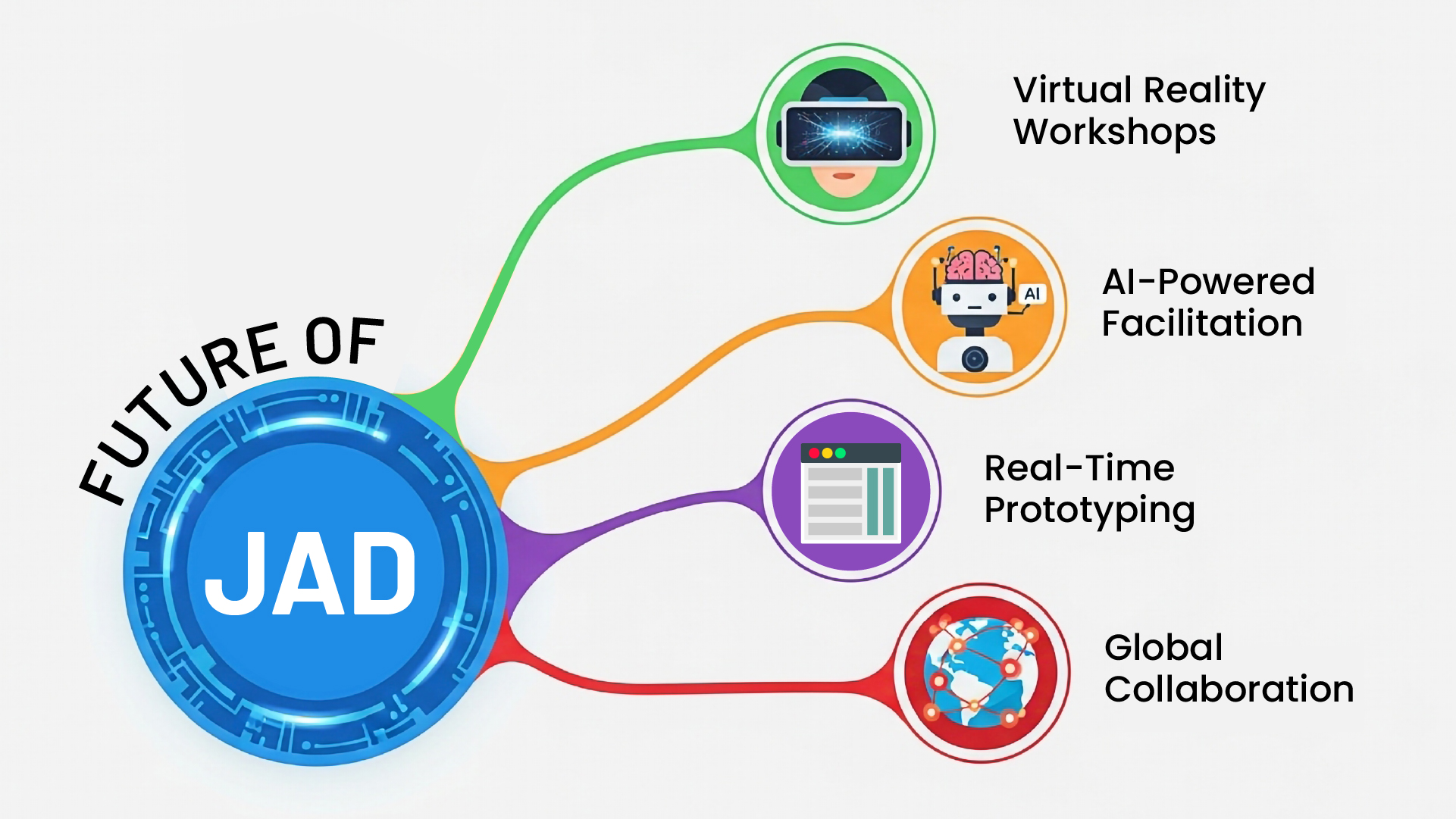
JAD in the Digital Age
Modern JAD implementations increasingly leverage:
- Virtual Reality Workshops: Immersive collaboration environments
- AI-Powered Facilitation: Automated meeting insights and action item tracking
- Real-Time Prototyping: Instant creation and modification of system mockups
- Global Collaboration: Multi-timezone workshop coordination
Integration with Modern Methodologies
JAD is evolving to work alongside contemporary approaches:
- DevOps Integration: JAD workshops informing continuous delivery pipelines
- Design Thinking Combination: User-centered design with structured collaboration
- Lean Startup Principles: Validated learning through structured user feedback
Conclusion
Joint Application Development remains a robust methodology for organizations seeking to improve software development outcomes through collaborative design and stakeholder engagement. While it was created in 1974, its principles of user involvement, structured collaboration, and consensus building are more relevant than ever in today’s fast-paced business environment.
The key to JAD success lies in proper preparation, skilled facilitation, and stakeholder commitment. When implemented correctly, JAD can significantly reduce development time, improve user satisfaction, and decrease project risk.
Ready to Transform Your Development Process?
Don’t let poor communication and disconnected stakeholders derail your next software project. Our team at Desol Int. specializes in implementing collaborative development methodologies that deliver results.
Contact us today to learn how JAD methodology can accelerate your development timeline while ensuring stakeholder satisfaction and project success.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How long do JAD workshops typically last?
JAD workshops usually run 3-5 consecutive days for comprehensive requirements gathering. The exact duration depends on project complexity and scope. Some organizations prefer shorter 2-3 day sessions followed by additional workshops as needed. The key is maintaining momentum and stakeholder engagement throughout the process.
2. Who should attend JAD sessions?
Essential participants include end-users, subject matter experts, developers, business analysts, and decision-makers with the authority to approve requirements. The ideal workshop size is 6-12 participants to ensure productive discussion while maintaining manageable group dynamics. Each participant should bring specific expertise or decision-making authority to the process.
3. What’s the difference between JAD and JAR (Joint Application Requirements)?
JAR (Joint Application Requirements) focuses specifically on requirements gathering, while JAD encompasses the entire collaborative development process, including design and validation. JAR is essentially a subset of JAD methodology, concentrating on the upfront requirements definition phase through structured workshops.
4. How does JAD handle changing requirements during the project?
JAD uses structured change management processes with formal evaluation and stakeholder approval. Changes are assessed for impact on timeline, budget, and existing requirements. The collaborative nature of JAD means changes are discussed with all stakeholders, ensuring informed decision-making about scope modifications.
5. Can JAD be used with remote teams?
Yes, JAD can be effectively implemented with remote teams using digital collaboration tools. Virtual JAD workshops use video conferencing, shared whiteboards, and real-time documentation tools. While face-to-face interaction is preferred, remote JAD can be successful with proper facilitation and technology support, especially in today’s distributed work environment.
